
SEO, Search Engine Optimization or Search Engine Optimization - you've probably heard these buzzwords from time to time. But what is behind it? What is SEO and why do you need it? You can read that and much more here. ... Continue reading
| 13 min |


| 16 min |
2010 May Day-Update
2010 Google Caffeine-Update
2011 schema.org-Update
2011 Panda-Update
2011 Freshness-Update
2012 Penguin-Update
2012 Pirate-Update
2012 EMD-Update
2013 Hummingbird-Update
2014 HTTPS-/SSL-Update
2015 Brand-/E-Commerce-Update
2015 Mobile-Update
2015 Newswave-Update
2015 RankBrain
2015 Phantom-Update
2016 Google Core-Update
2017 Fred-Update
2017 User Localization-Update
2018 Speed-Update
2018 Medic-Update I + II
2019 BERT-Update
2021 Page Experience Update
2022 Google Core Update
2023 Google Helpful Content
2024 Android features
Google regularly updates its algorithms through both date refreshes and updates. While data refreshes are changes to the database with which the algorithm works, updates consist of an actual change to the algorithm. We have summarized the most important updates of the last few years for you.
The update rolled out in May 2010 (hence the name) has a particular impact on Google’s ranking algorithm. Long-tail keywords in particular were targeted. Like virtually all Google updates, this one is again aimed at answering search queries better and thus increasing the quality of search results. Especially, keywords with a length of three to four words usually have a high conversion rate. Pages that fell into this range were therefore frequently affected.
The consequence of this update: “Large” websites that have ranked with less suitable content on long-tail keywords to date are to be downgraded in the SERPs. The quality thus increases, and the search results are more accurate and helpful for users.
This update primarily dealt with web content indexing and made changes to the search index infrastructure. As a result, the search index can be updated faster and, compared to the previous one, allows for a continuous crawling process.
In 2011, Google, Yahoo and Microsoft decided to work together and agreed on common rules that were recorded on schema.org. These are thus read out during indexing, which in turn makes it possible to display additional information in the form of rich snippets in the search results, for example. Through the update, it was thus decided that all search engines adhere to these indexing rules.
This update focuses on website content that is as high-quality as it is unique and that has added value for the user. As a result, both dubious content and content of inferior quality are penalized and therefore receive a lower Google ranking. Even today, the Panda update is regularly expanded and updated with additional signals. This makes the filter even finer and makes it easier for the algorithm to distinguish between good and bad content.
Freshness is another name given to a Google update. The naming subtly points to its goal: Topicality of search results. However, not every search query relies on a result with up-to-date content. Therefore, it was necessary to categorize them. Therefore, there is the following classification:
| Recent Events Hot Topics | Regular Updates | Frequent Updates |
| Current, timely and/or hotly debated topics | Regularly recurring events → not permanent, but recurring | Topics with frequent changes |
The basis for this update was the Google Caffeine update.
In addition to the Panda update, Google has refined its algorithm with the Penguin update. Again, this is a quality filter that penalizes misbehavior. While the Panda update checks website content, the Penguin update takes care of identifying spam, linking, keyword stuffing and unnatural backlink patterns. Again, as with the previous update, regular updates are made. This update is the most important one for link building, as it aims to penalize especially unserious and unnatural link building.
The pirate update, named after piracy, penalizes sites that violate copyright. Websites that offer illegal content, such as pirated copies or similar, can thus be penalized, with the result that they disappear partially or even completely from the SERPs.
EMD is the abbreviation for Exact-Match Domain. This is a change to Google’s ranking algorithm, which is intended to improve the search results displayed. In response to a search term, users therefore only receive matches that are as close as possible to exact matches. Keyword domains with thin content, i.e. very thin and poor quality content, are downgraded in the ranking.
Answer users’ search queries more specifically with better content.
In 2013, Google search turned 15 years old. Fittingly, the search engine integrated a completely new generation of the algorithm, which has been the basis of all search queries since then. With the Hummingbird update, Google took a big step towards understanding semantic search queries. This means that the search is more targeted and the actual connection between the keywords and the user’s intention can be better interpreted. Especially interrogative phrases (“How will the weather be in Munich?”) or search queries in entertainment form (“Show me pictures of the Statue of Liberty.”) are more clearly assigned by the update.
As the name suggests, this update provides for a higher weighting of HTTPS encryptions. Since then, these have been considered a ranking factor. This in turn gives webmasters the incentive to provide more security on the net. SSL certification confirms the identity of the domain and guarantees the user a secure connection.
Even though this update was never really confirmed, it had a great effect. A strikingly large number of well-known brand websites and online stores have benefited from this update, which probably earned it its name. Particular focus was placed on keywords with high search volume.
Today, it’s hard to imagine life without the smartphone, but that wasn’t always the case. In 2015, Google decided to jump on the growing trend of mobile search and make it easier for users to search via smartphone. The main consequence of this update was that websites gradually had to make a mobile adaptation in the form of a responsive design or a mobile website in order to rank well.
This update played into the hands of news websites in particular. It was carried out by Google without much fanfare and was never officially communicated. As with the Freshness update in 2011, the goal is to keep the search results up to date. This time, however, the focus is on trending keywords and information-oriented short head keywords.
If you talk about Google updates, you can’t avoid RankBrain. This is machine learning, or artificial intelligence, which has been integrated into the algorithm as a subsection. The AI helps to better process and understand search queries that were never there before. This update does so with one goal in mind: better analysis of search queries so that relevant web pages are served up even if they don’t match the exact wording of the search query. Here’s what RankBrain can do:
The phantom update is an update not communicated by Google – it was thus introduced silently and secretly, hence the name. However, this is not the first phantom update, as there were other non-communicated “phantom updates” both in years before and after. The focus in 2015 is on the quality signals of the Core Algorithm and user intentions. Since Google’s side never commented on this update, there are various speculations about content and the connection with other updates. The most persistent one: RankBrain and the Phantom update are directly connected. This rumor arose mainly because both were launched within a relatively short time and both focus on user intent.
The first of many core updates was rolled out in 2016. The result: High-quality and holistic content that encompasses and illuminates a topic holistically is better placed within the SERPs. But in addition, an appropriate response to user intent now also plays a role.
There was also a change to Google’s core algorithm with the Fred update. Once again, the ranking criteria were optimized to further increase the quality of page content. As is customary for Google, the focus is on added value for the user. The consequence of this update was that pages with outdated or thin content were penalized. In addition, texts that were over-optimized with keywords from a pure SEO perspective were also devalued. The Fred update therefore attacks, similar to Panda and Penguin, pages that are not designed for the benefit and added value of the user.
Those who were used to simply solving queries in foreign countries by providing the URL of Google with the corresponding country code Top Level Domain (ccTLD) (for example, instead of www.google.de simply the Spanish version www.google.es), fail since this update. In the meantime, the search engine localizes your physical location and displays suitable results from your surroundings accordingly. You will notice this particularly well if you are on vacation and make search queries there.
Page speed has long been one of the most important ranking factors. Since the update in 2018, it has been weighted even more heavily – especially for searches on mobile devices. This shows Google once again how indispensable mobile traffic has become. Through various tools, such as Pagespeed Insights, webmasters can check the loading times of their website and optimize it accordingly.
You want to learn, how to optimize your pagespeed? Have a look here!
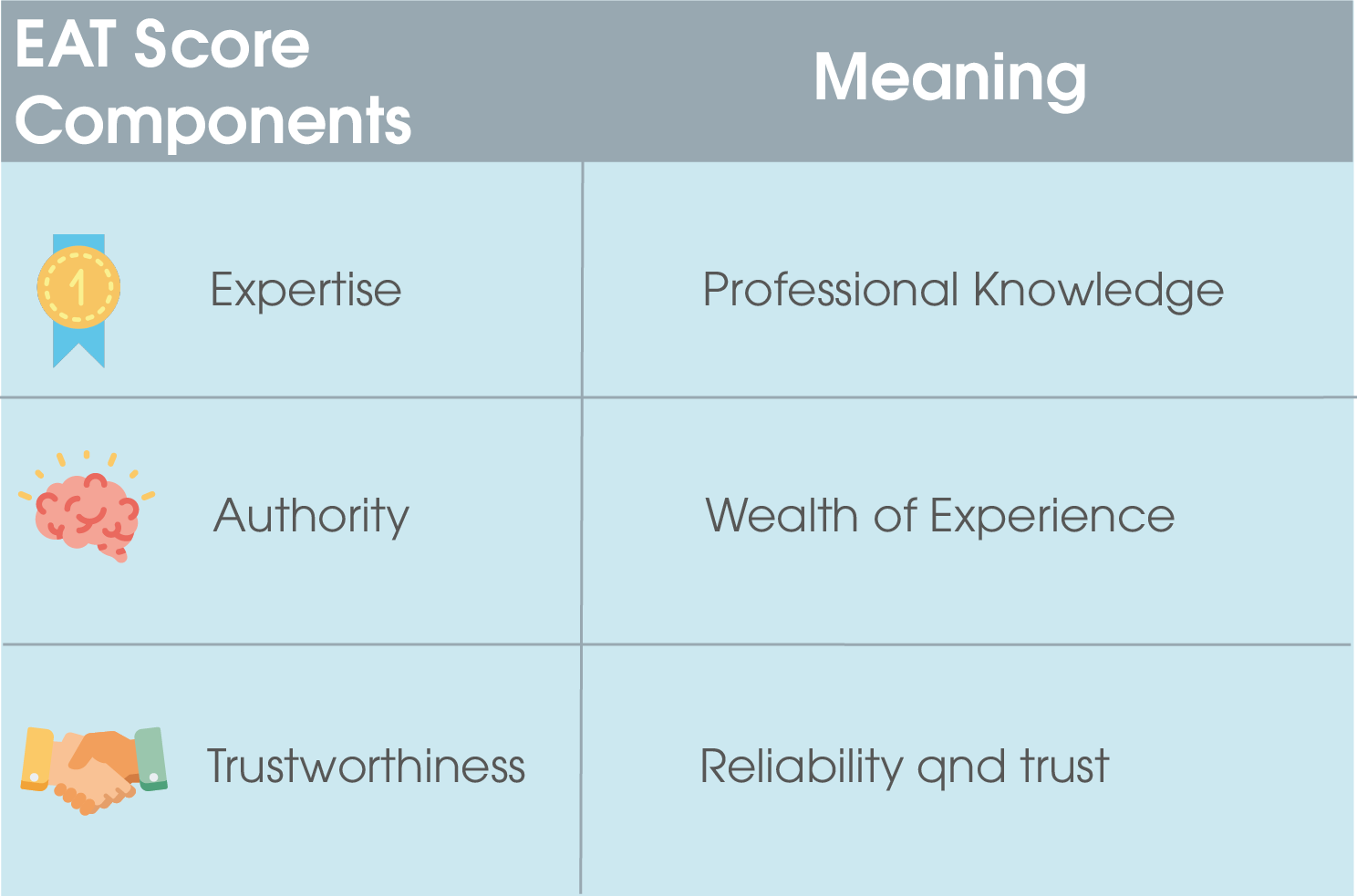
The Medic update was launched in August 2018 and updated again in October. Like the Fred and Phantom updates, it affects the core algorithm. The naming comes from the fact that the first launch unmistakably affected many sites in the healthcare sector. Not only that, various YMYL sites (“Your Money, Your Life”), i.e. financial, fitness and wellness sites, were also impacted. What is striking here is that these are primarily websites with sensitive content that can have a direct influence on the user. Thus, it is clear that this update aims to identify the trustworthiness of a page and ensure reliable content. With the three points of the Google E-A-T score, it is very easy to check how reputable your page is.
The latest update from Google is the BERT update. This is an innovation that ensures that the search engine can better understand Natural Language Processing contexts of the language. This makes it possible for complex contexts, such as long-tail search queries, to be better understood. Above all, Natural Language Processing helps the search engine to understand the semantic context. It began with a rollout in the USA, and BERT has also been available in Germany since December 2019.
In May 2021, Google will introduce the Page Experience Update. In the process, the previous ranking factor PageSpeed will become a new metric: the Core Web Vitals. These in turn are divided into three components:
With the help of these, the PageSpeed factor is made more measurable. This should make it easier to assess the performance of a page.
In 2022, Google focused on the further development of search technology and the improvement of visual search through significant updates. A core aspect of these updates was the introduction and enhancement of Google Lens and Multisearch, which allowed users to utilize their surroundings or images for searching, thereby creating a more natural interaction with the search engine. Based on advances in machine learning, these updates aimed to redefine the way people search for and explore information. They made it possible to make visual queries and add text to images to obtain detailed and contextually relevant search results. Thus, the year 2022 marked a significant step by Google to make visual search more intuitive and to expand search beyond the traditional text box.
In 2023, Google rolled out the “Helpful Content Update,” a significant update aimed at further improving the quality of search results by favoring content that is primarily helpful and informative to people. Although this update was not explicitly mentioned in the provided sources, it aligns with Google’s long-term goal of enhancing user experience by rewarding websites that offer valuable, user-centric content.
Updates such as the Core Update conducted in March 2023 and other initiatives to revise review systems demonstrate Google’s commitment to promoting high-quality and relevant content. These updates highlight the importance for website operators and SEO experts to focus on creating content that provides real value to users to rank well in search results.
Google’s “Helpful Content Update” sets clear no-gos to enhance the quality of search results and promote content primarily created for people, not search engines.
By steering clear of these no-gos and focusing on creating valuable, people-first content, you can align your content strategy with the objectives of Google’s “Helpful Content Update” and improve your chances of ranking well in search results.
In 2024, Google introduced significant updates aimed at enhancing the user experience in search and device connectivity. One notable update is “Circle to Search,” a new feature that allows users to search for information directly from their Android phone screens without needing to switch apps. By simply circling, highlighting, or scribbling on images, texts, or videos, users can instantly search for related information. This feature has been launched globally on select premium Android smartphones, including the Pixel 8, Pixel 8 Pro, and the Samsung Galaxy S24 series.
Another major update is the expansion of multisearch in Lens, enabled by recent advancements in generative AI. This update allows users to pose more complex questions by pointing their camera at an object or uploading a photo, thereby enhancing the ability to search using both images and text. The AI-powered multisearch provides insights beyond mere visual matches, making it easier for users to explore the world and find relevant information from across the web.
Furthermore, at CES 2024, Google announced updates across the Android ecosystem designed to improve device interoperability and the user experience. These updates include a new way to share files across devices using Quick Share, the expansion of Fast Pair support to more devices for easier Bluetooth connectivity, and casting capabilities for more apps and devices, such as casting TikTok content to Chromecast built-in devices. Google also emphasized the importance of Matter for creating greater interoperability among smart devices in homes.
Additionally, Google is enhancing its data portability with updates to Google Takeout, including direct data transfer capabilities for YouTube. This initiative aims to facilitate the export of data to third-party operators and enable direct service-to-service data portability, as part of Google’s commitment to improving data mobility and user control over their data.
These updates reflect Google’s ongoing efforts to improve search functionality, device connectivity, and data portability, offering users more intuitive, seamless experiences across its services and devices.
We'll tell you how to optimize your website for search engines.


