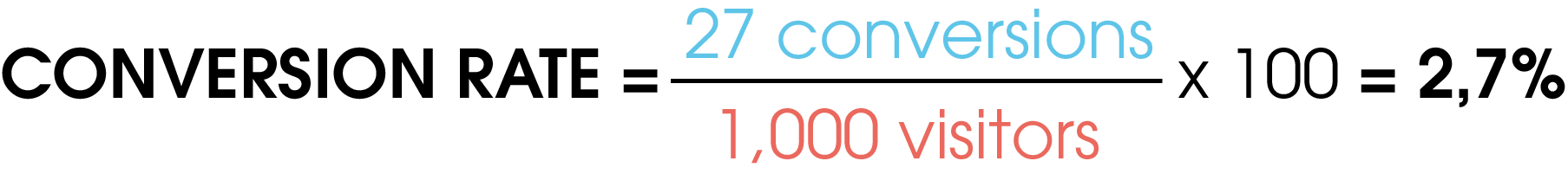What is a conversion?
In order to answer the question “What is the conversion rate?”, we first need to clarify what a conversion is in the first place. Conversion means ” transformation” and means in most cases the conversion of a visitor into a customer. What exactly a conversion looks like depends on the goals of the website operator. A conversion is said to occur when a website visitor performs the action intended by the website operator, thus achieving his or her desired goal. Here are a few examples of possible conversions
- Registration on a website
- Completed purchase of a product
- Registration for a newsletter
- Submitting a contact form
- Clicking a CTA button
- Download of a product
But also so-called soft conversions, such as clicking on the phone number or on the email address, are possible to count smaller completions.
What is the conversion rate?
The conversion rate is therefore the metric for measuring conversion. It is an important key performance indicator (KPI), i.e. a performance indicator that represents the percentage relationship between the number of visitors to a website and the conversions that occur.
Why is the conversion rate so important?
Conversions are counted for Google Ads, among other things, in order to find out how successfully the ads are performing. If you have a low CR, for example, this may indicate that your content is not suitable for the ads placed or that you are not convincing the customer enough to make the desired conversion. The CR is therefore important to find out whether the ads you are running (and the money you are spending on them) are worth it or whether you would rather put the budget into other advertising opportunities.
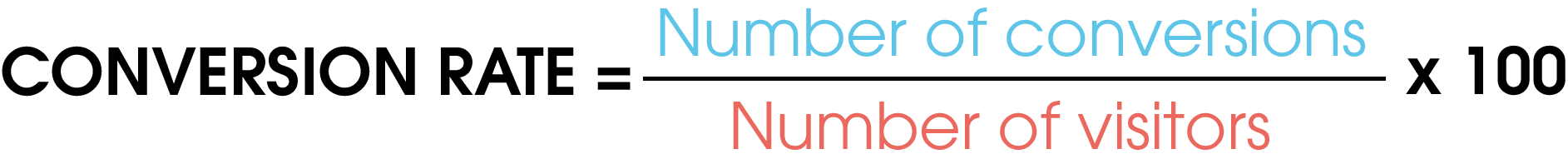
How is the conversion rate calculated?
The CR is a percentage that you calculate as follows:
If, for example, 27 customers out of a total of 1000 make a purchase in an online store, the result is a CR of 2.7%.
How high should a good conversion rate be?
There is no general answer to how high a good CR is. This depends on various factors. Depending on the industry and business model, the level of the CR can differ. In addition, the price, the products offered or even the season influence the CR. Online stores that sell very expensive and exclusive products, for example, naturally have a lower CR than online stores that offer rather inexpensive products for the average consumer. In e-commerce, an average CR of 1% is assumed. This means that every hundredth customer in an online store completes a purchase. However, for successful online stores, the CR can be quite higher, sometimes even up to 10%.
Common reasons for a poor conversion rate
There are several factors that can have a negative impact on the CR. Below you will find a few examples that you should try to avoid:
- Unserious looking website (for example grammatical and spelling mistakes)
- Lack of trust (for example trust symbols, seals of approval)
- Missing payment options (for example PayPal)
- Technical problems (e.g. redirection to the payment service provider)
- Poor usability
- Poor pagespeed (very long loading times)
How do I optimize my conversion rate?
To improve your CR, you can make general adjustments to your website. For this, it’s best to take a look at our article on OnPage optimization. There, we explain how to perform technical, content and structural measures on your website. Try to avoid the examples mentioned above. Regarding your paid ads, you can improve your ad texts to attract the interest of your customers. Good headlines and texts will encourage potential customers to click on your ad. You should also adjust your target groups so that your ads are played out to the right group of people. Optimize your keywords and check if you can add relevant keywords.