Golden Circle marketing model for marketing products and services. Find out how the model works here with us! ... Continue reading


Simply put, the frontend is what you see “in the foreground” – the user interface. A frontend exists for CMS-based websites. Here, all visible content, i.e. the design, the layout of the website, images, texts, etc. are displayed via the frontend. It contains everything that you can actually see when you click on a website. But that’s not all: every software and every computer game also has a user interface that the user sees and uses to enter commands. This is also called the frontend. The backend, on the other hand, is everything that happens in the background and is thus invisible to the user. The frontend is thus the user-friendly translation of the source code stored in the backend.
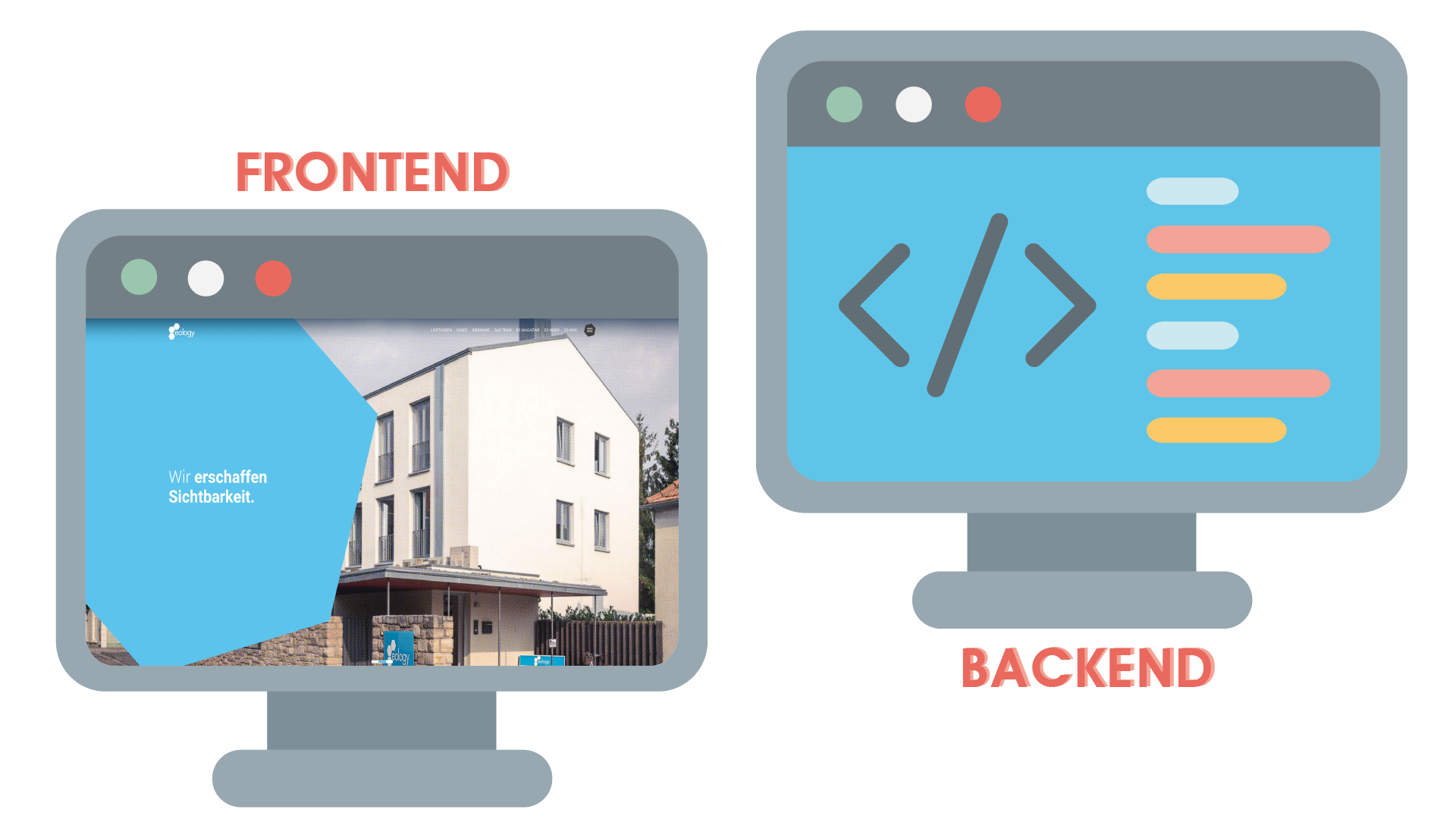
IT systems are divided into two parts in a kind of layered classification: frontend and backend. The frontend is the layer that the user sees, which is why it is also called the presentation layer. It is therefore close to the user and enables access to data and processes. This data is in turn stored in the backend and the processes are processed there. You can think of the backend as a database that operates in the background while the frontend takes over the graphical representation in the foreground.
Remember: Without backend, no frontend!
You can modify the frontend of your website using CSS, JavaScript and other programming languages. Thus, it gets more functions, which adjust the visualization according to your wishes. In addition, the frontend can influence the following areas:
If you want to optimize your conversion rate, you should take a closer look at your frontend. Fact is: The conversions of your users are significantly influenced by the design of your website. If your site is not designed in a user-friendly way, your website visitors will get lost due to poor navigation, for example. The chance that they will not convert is much higher. Improvements in loading time and caching optimization are also part of the frontend.
The frontend can influence the rating of your website by the search engine. When building it, you can make sure that it becomes SEO friendly. There are several factors that belong to the frontend and that you should consider.

If a page is user-friendly, structured and easy to understand, it invites you to stay. This improves both the dwell time and the bounce rate of your website visitors – both are important evaluation criteria of your website.
Only if your HTML code is error-free, the page can be crawled correctly and completely. The consequence would be that the page is not indexed.
Unique content is always important. Content on your page should be unique – that is, it should not duplicate content on your own website or on another website. So-called duplicate content leads to the fact that search engines cannot clearly differentiate who is the author of the content. Thus, it cannot be decided which page is the really relevant one and therefore cannot be indexed.
Flash content and frame sets should be avoided because they cannot be crawled by search engines. However, both are methods that are no longer regularly used today.
An individual page title and a customized meta description is important for every single one of your web pages. They help search engines to rank the page.
Internet users are often impatient. A long loading time therefore leads to a more frequent bounce. You can test how fast your page is using Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool, for example.
Breadcrumbs help users find their way around the website. They leave a breadcrumb trail, so to speak, by which the user can trace his already “stepped” path. This type of navigation increases user-friendliness.
With internal links you help search engines to better understand your site and its structure.
With the Robots.txt you tell the search engine which pages should not be crawled. This is especially advantageous for you, because you save your crawling budget, which is limited for each website.
An XML sitemap can be seen as a table of contents of your website. It tells the search engines how extensive your website is and helps them to crawl your website completely.
The URL is not only important for the search engines, but also for the orientation of the user. If your user can understand where the URL is leading him, it increases the usability.
Never miss the hottest news again.