The Robots.txt is used to control the crawling behavior of bots. What it has to do with it you will learn here with us! ... Continue reading


Semantics, a core concept in linguistics, refers to the study of meanings in signs, words and symbols. The word comes from the Greek and plays a crucial role in the world of search engine optimisation (SEO). The key point is the relationship between signs and their meaning and there are three basic forms of semantics:
Linguistics and thus the understanding of languages is the area relevant to search engine optimisation. The reason for this is that every user behaves individually on the Internet and searches for things in their own way. As there are many different words that often have the same meaning, search engines rely on semantics (SEO semantics) to always display the most relevant results in the SERPs.
A semantic search analyses and focuses on the meaning of the search query. It is no longer just about keywords, but about the connections between the words. Keyword-based search engines only deliver results that match the corresponding keywords. Semantic search engines, on the other hand, look at the contextual connection of the search query. This helps to deliver more accurate and relevant search results. Semantics are intended to mimic the human brain and ‘understand’ the search query.
The difference is therefore relatively simple. While keyword-based search engines always display the pages that contain the most relevant keywords in the top positions, semantic search engines use what is known as an algorithm. This establishes relationships between words, phrases and sentences and develops an understanding of connections. This helps you to obtain more relevant and accurate results. For example, if you ask a semantic search engine a question, it searches specifically for the answer, while a keyword-based search engine searches for the keywords of the question.
There are two factors that influence semantic analyses:
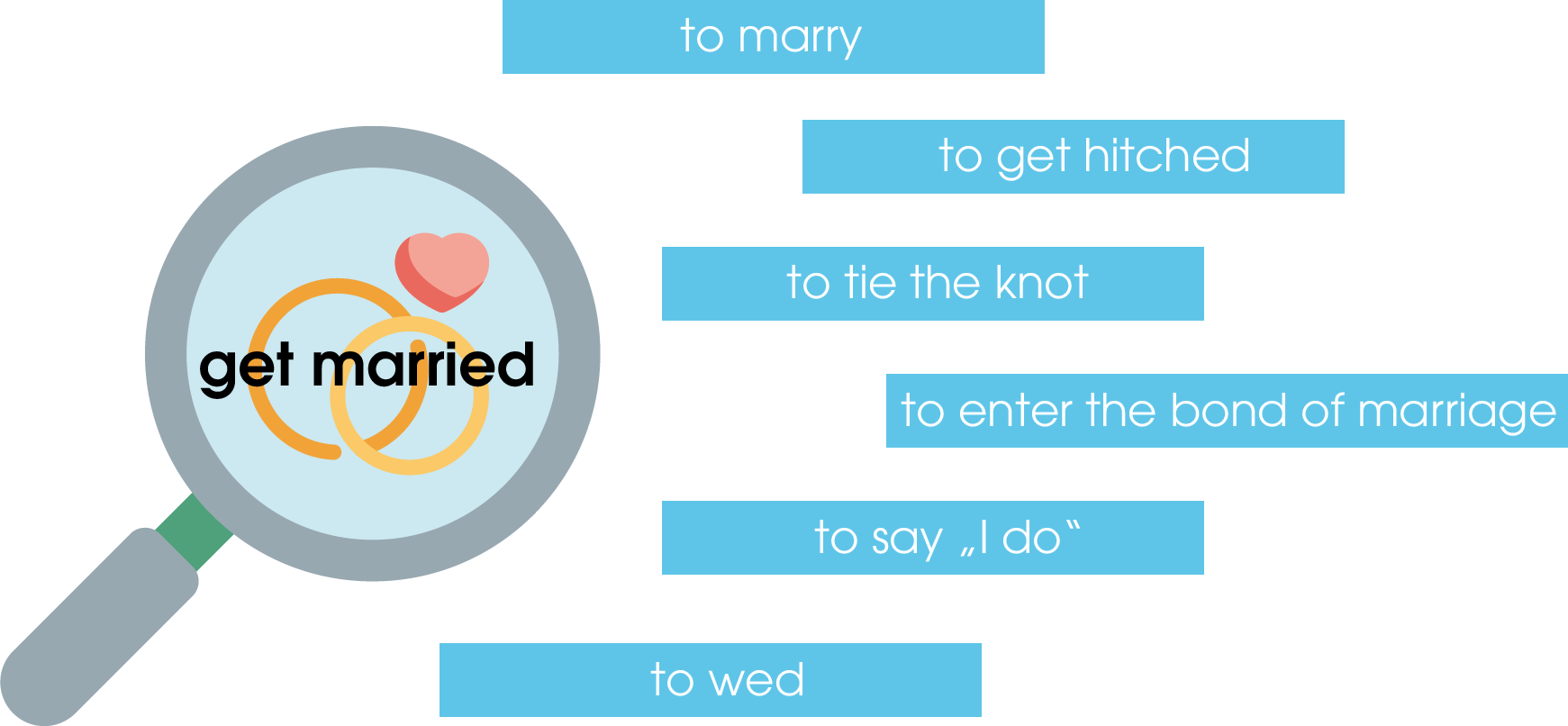
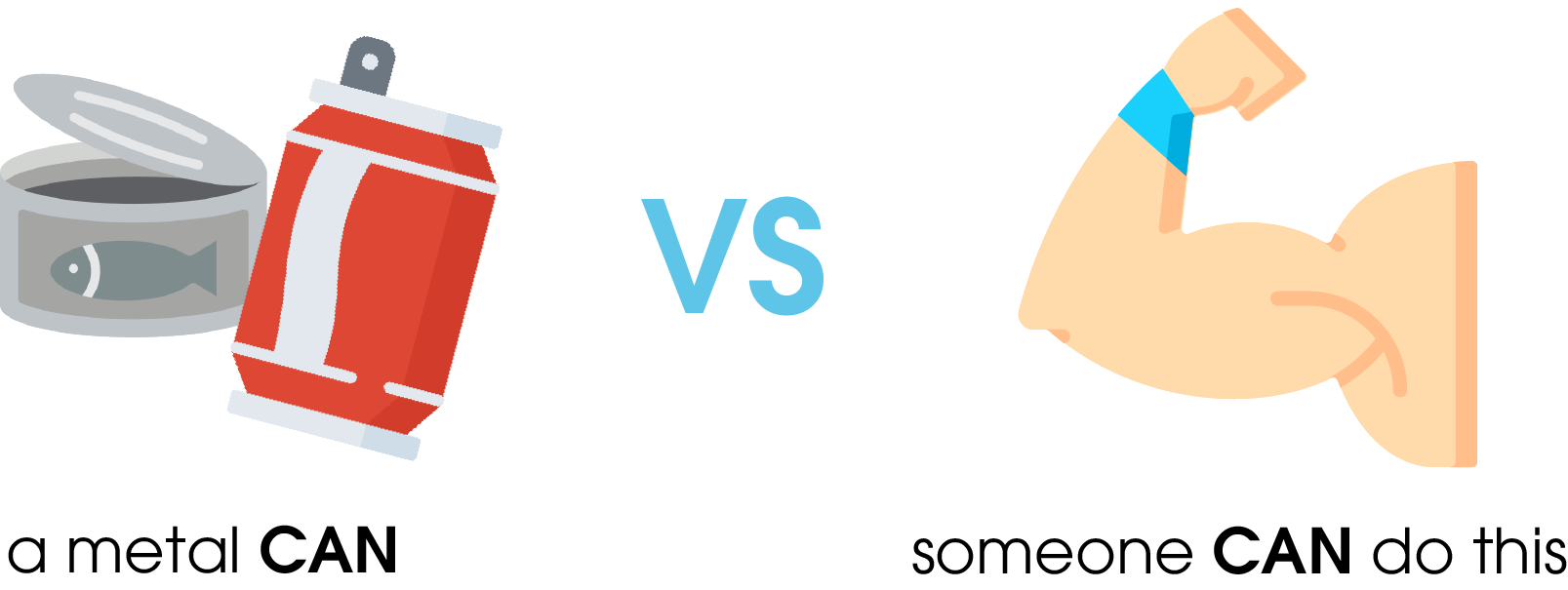
Synonyms are always included in semantic searches, while homonyms with an inappropriate context are excluded from the search results. To be able to do this, the search engine bot needs background knowledge. This works with the help of machine learning.
The advantages of semantic analysis are clear:
Of course, a semantic search also has its limits. For example, if you enter a fairly generic search term such as rabbits in the search bar, you will get a wide variety of results, most of which you probably don’t need. You’ll find results on the differences between hares and rabbits, various videos and products with and for hares.
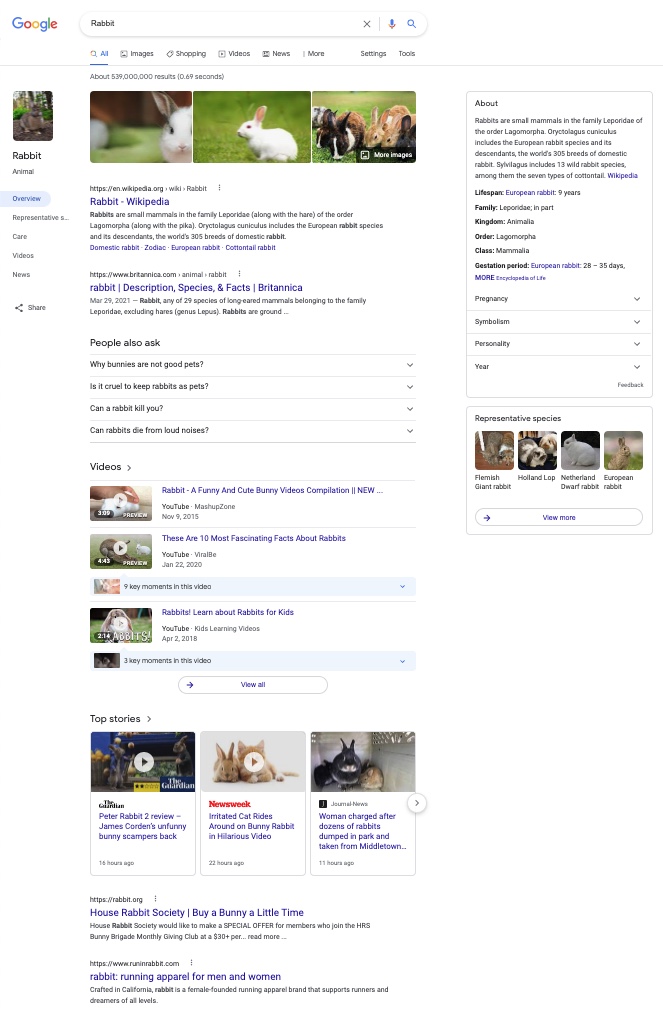
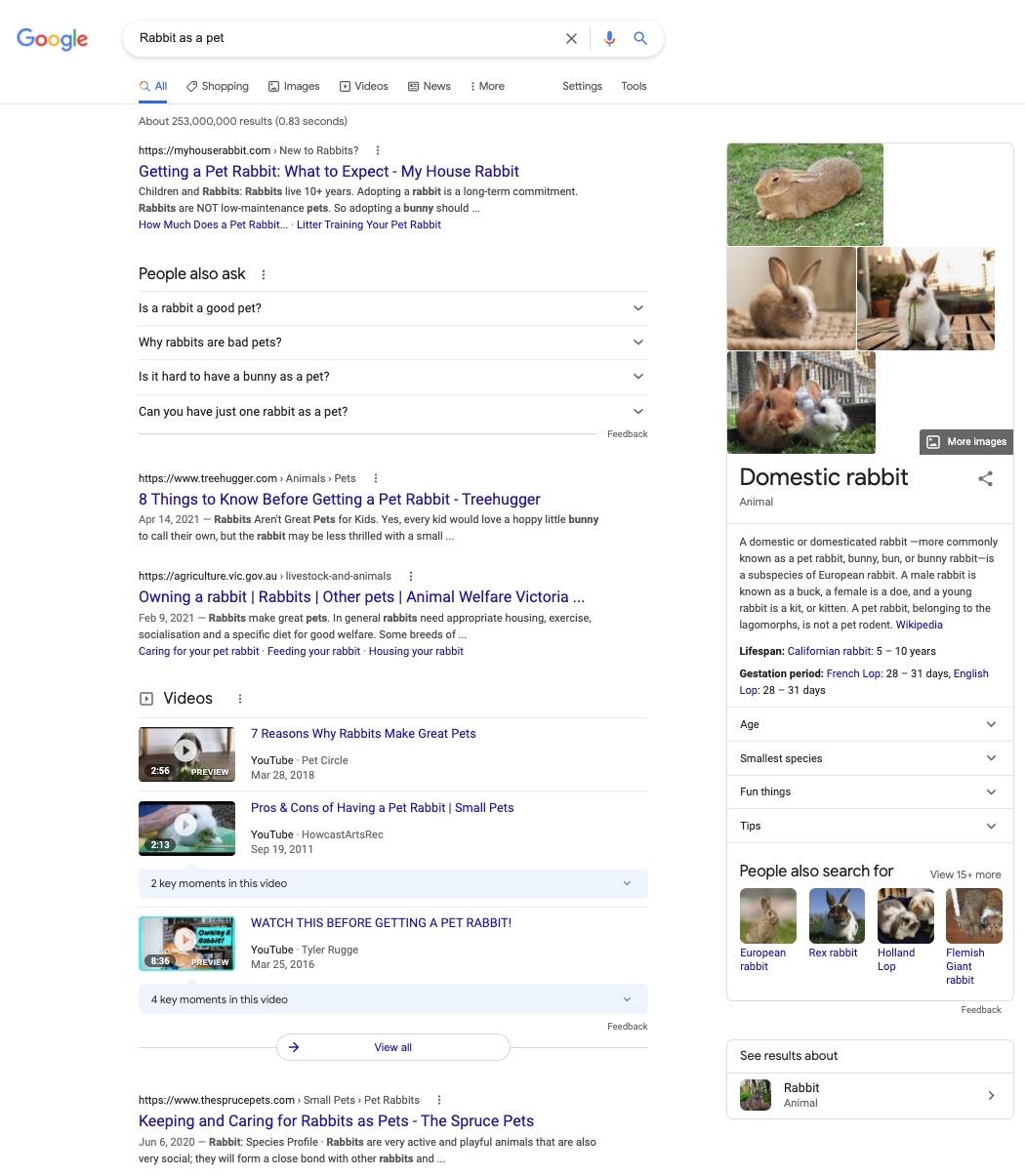
You won’t find any information on what you need to consider, for example, if you want to keep a rabbit as a pet. However, the search engine cannot guess that this is exactly what you want to know. In this case, the algorithm needs further information that it can interpret. That’s why long-tail keywords are better in this case. This allows the search engine to interpret more information in your search and better analyse correlations. As a result, you really get what you want to know.
Therefore, if you enter ‘rabbits as pets’ in the search bar, you will receive precise results that answer your question. You could also go into more detail and, for example, search for ‘Which rabbit can I keep as a pet’ or ‘How do I keep a rabbit properly’. However, this is sometimes not even necessary, as the algorithm can already understand the results relatively well and displays what is most relevant in this context.
Definitely yes! It is clear that semantic searches will definitely continue to characterise the search engines of the future. But even now, the algorithms of Google, Bing and co. are already well on their way and work heavily with semantics. That’s why you should make sure that you don’t just use hard keywords in your SEO content, but also semantic keywords that increase relevance.
Semantic keyword research is the targeted analysis of keywords that increase the relevance of your content. Semantic keywords are therefore the keywords that are most associated with your main keyword. They help the algorithm to interpret the content more easily and deliver more precise results to users. To carry out semantic keyword research, it is best to use a WDF*IDF tool. This will then provide the words that are most frequently contained on comparable landing pages with similar content to yours. If you then incorporate these words into your texts, this increases the relevance of your text and improves comprehension for the search engine. At best, this will also have a positive effect on your ranking.
You want to learn more about exciting topics?